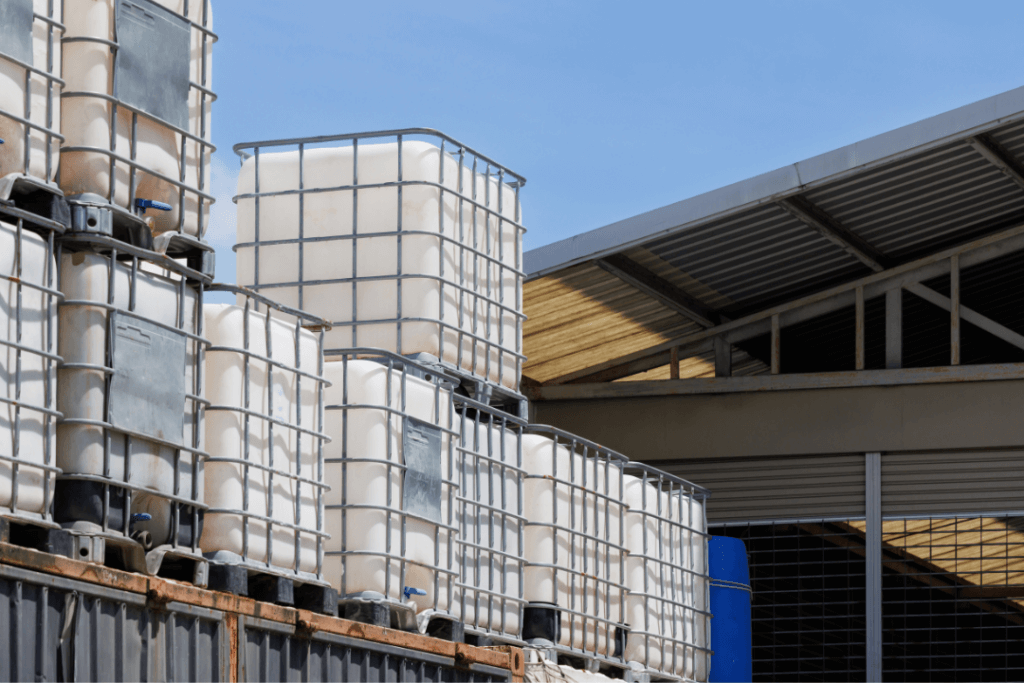
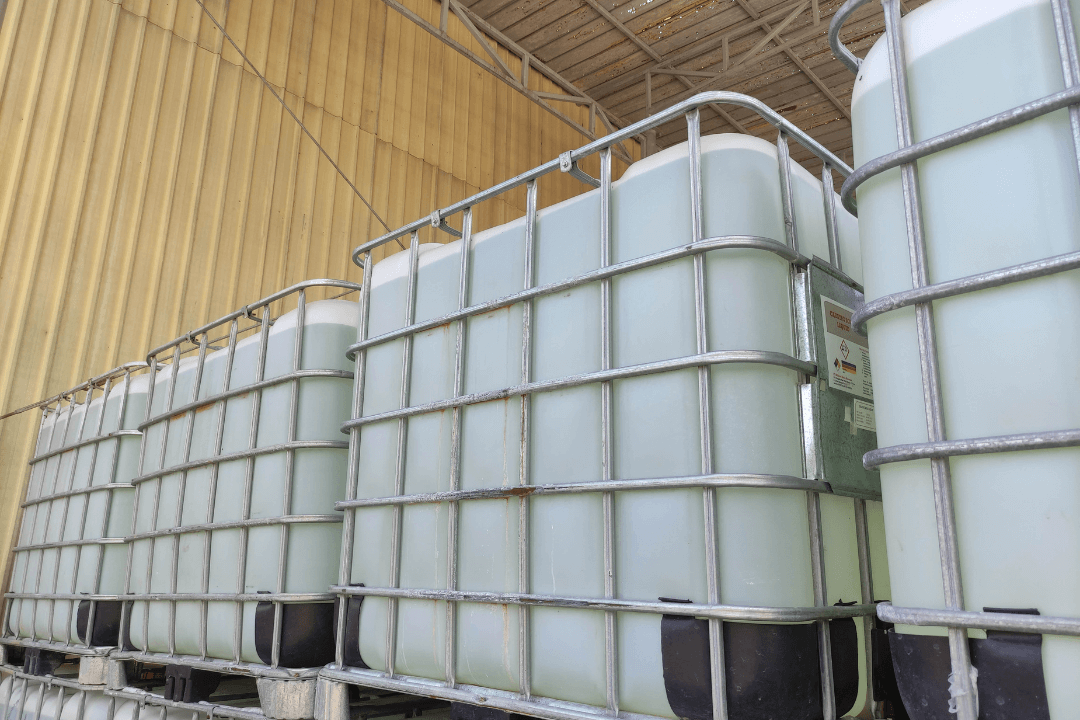
When it comes to packaging solutions for bulk materials, businesses across various industries rely on Intermediate Bulk Containers (IBCs). These versatile containers are designed to safely store and transport liquids, powders, and granular products in large quantities. At C.L. Smith, we specialize in providing a wide range of IBC options tailored to meet the needs of different sectors. In this blog post, we will explore the different types of IBCs, the materials used in their construction, typical capacities, and how to choose the right IBC for your business needs.
Table of Contents
- What are Intermediate Bulk Containers (IBCs)?
- Types of IBCs
- Materials Used in IBC Construction
- Typical Capacities of IBCs
- Advantages of Using IBCs
- Choosing the Right IBC for Your Needs
- Sustainability & Reconditioning Services
- Making the Right Choice for Your Bulk Packaging Needs
What are Intermediate Bulk Containers (IBCs)?
Intermediate Bulk Containers, or IBCs, are large, reusable containers used to store and transport bulk liquids, chemicals, and dry goods. Typically made of rigid or flexible materials, IBCs come in various shapes and sizes to accommodate different types of products. They are designed to meet the specific needs of industries such as chemicals, food & beverage, pharmaceuticals, and more.
At C.L. Smith, we understand that choosing the right IBC is crucial for your logistics and operations. That’s why we offer a wide selection of IBCs to ensure your goods are transported safely and efficiently.
Types of IBCs
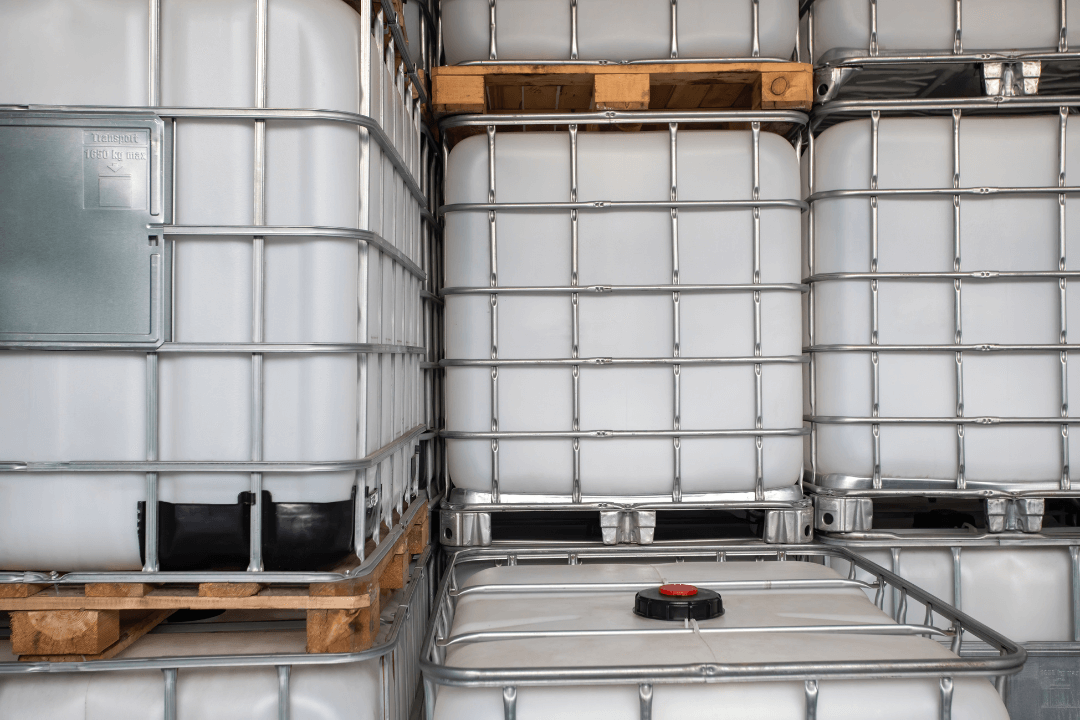
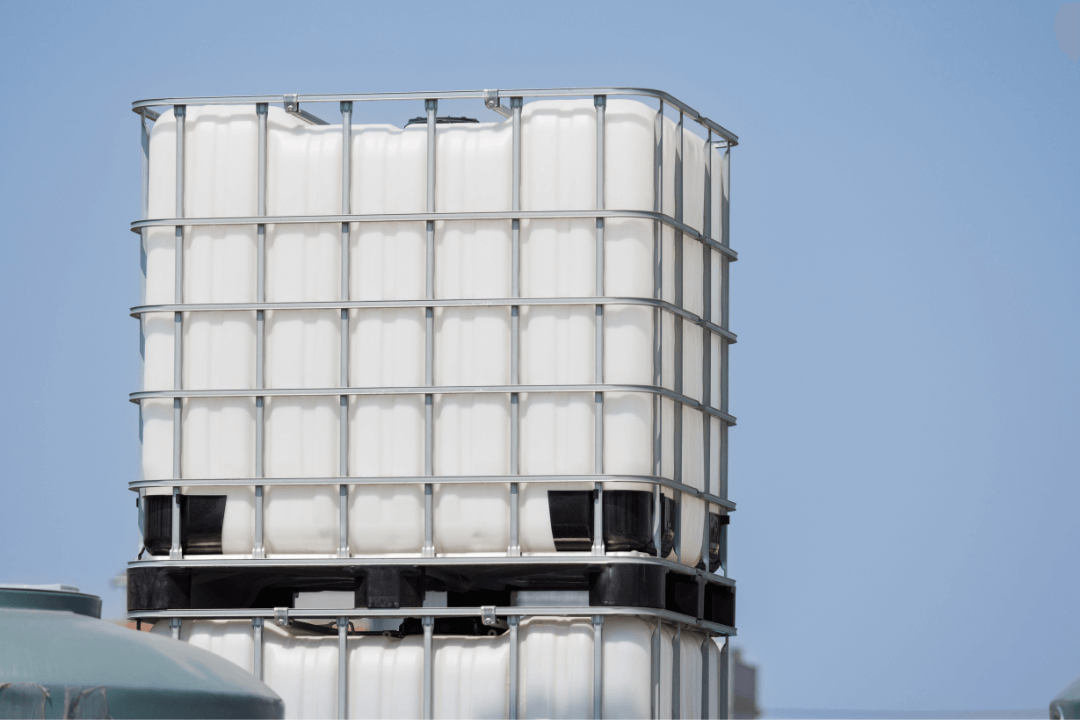
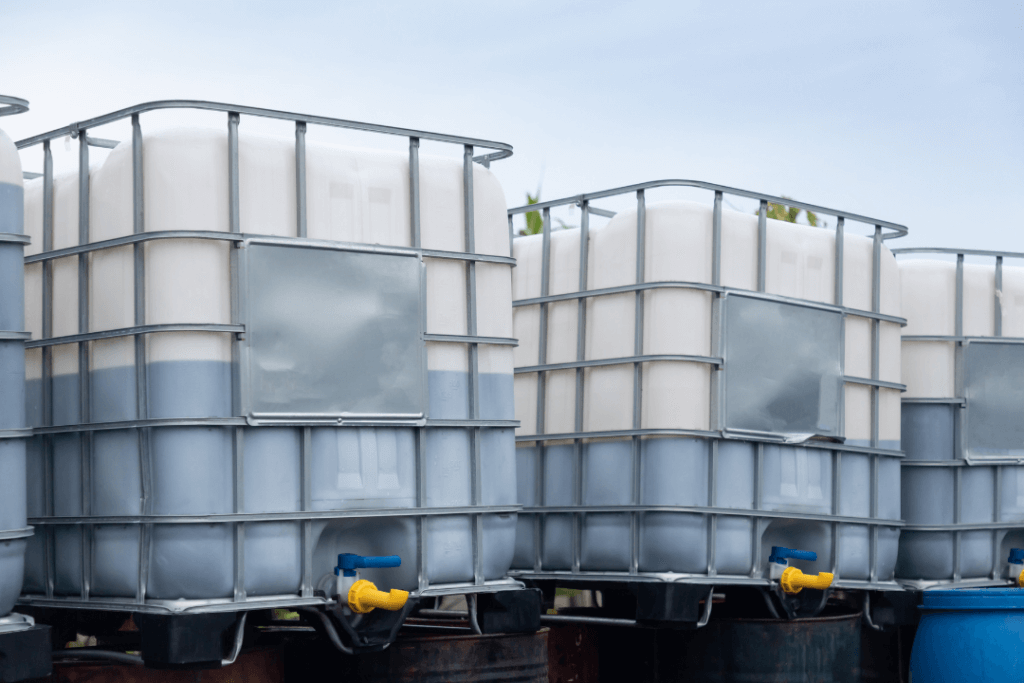
- Rigid IBCs:
Rigid IBCs are the most common type of bulk container. They are typically made of high-density polyethylene (HDPE) or stainless steel and are designed to handle heavy-duty applications. Rigid IBCs are durable and offer excellent protection for products during transit. They are ideal for industries such as chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and food & beverage.
- Material Options: HDPE, stainless steel, carbon steel.
- Typical Capacity: 275-330 gallons.
- Applications: Used for storing and transporting chemicals, oils, detergents, and food ingredients.
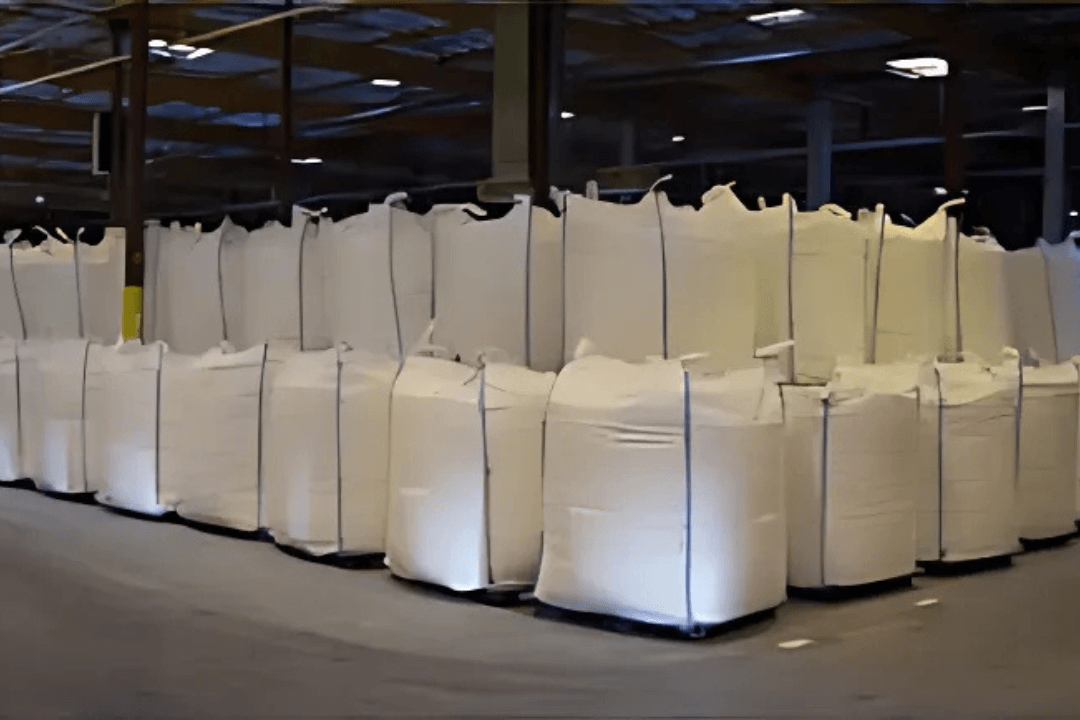
- Flexible IBCs:
Flexible IBCs, also known as flexible intermediate bulk containers (FIBCs) or bulk bags, are made from woven fabric materials such as polypropylene. These containers are designed for lightweight, bulk storage and transport, making them a cost-effective option for many industries. Flexible IBCs are often used for dry powders, grains, and other non-liquid products.
- Material Options: Polypropylene (PP) fabric, PVC coatings.
- Typical Capacity: 1000-4000 pounds (dry goods).
- Applications: Ideal for the agriculture, construction, and food industries, especially for dry powders and granules.
Materials Used in IBC Construction
The material used in the construction of an IBC plays a vital role in determining its suitability for a particular application. Different materials offer varying degrees of strength, chemical resistance, and safety features. Here’s a breakdown of the most common materials used in IBC manufacturing:
- High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE):
HDPE is a robust, corrosion-resistant plastic material commonly used in the construction of rigid IBCs. It is well-suited for storing a wide range of chemicals, including those that require high resistance to corrosion and impact.
- Stainless Steel:
Stainless steel IBCs offer superior durability and resistance to high temperatures and aggressive chemicals. These containers are often used in the pharmaceutical and food industries due to their high cleanliness standards.
- Polypropylene (PP):
Polypropylene is the most common material used for flexible IBCs. It is lightweight, durable, and resistant to a wide range of chemicals, making it ideal for dry bulk storage and transportation.
Typical Capacities of IBCs
IBCs come in a variety of sizes to suit different storage and transportation needs. The most common capacities for rigid IBCs range from 275 to 330 gallons (1040 to 1249 liters), making them ideal for industries with bulk liquid requirements. For flexible IBCs, the typical weight capacity ranges from 1000 to 4000 pounds (453 to 1814 kilograms), making them suitable for dry goods like grains, powders, and fertilizers.
At C.L. Smith, we offer both rigid and flexible IBCs with varying capacities to ensure that your specific packaging needs are met.
Advantages of Using IBCs
- Efficient Storage & Transport:
IBCs are designed to maximize storage efficiency while minimizing transportation costs. Their stackable design and large capacity reduce the number of containers needed for bulk shipments, making them an environmentally friendly choice for bulk packaging.
- Durability:
Both rigid and flexible IBCs are designed to withstand the rigors of long-distance transportation and harsh environments. Whether you’re shipping chemicals or food products, IBCs provide the protection and durability needed to prevent damage during transit.
- Reusability:
One of the main advantages of IBCs is that they can be reused multiple times, making them a more sustainable and cost-effective alternative to single-use packaging solutions. Additionally, IBCs are designed to be easily cleaned, making them ideal for industries with stringent hygiene requirements.
Choosing the Right IBC for Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate IBC for your product involves considering several key factors, including the nature of your product, regulatory requirements, and budget. Here are a few tips for making an informed decision:
- Product Characteristics: Consider whether your product is a liquid, powder, or granular substance. Rigid IBCs are best for liquids, while flexible IBCs are ideal for dry goods.
- Chemical Compatibility: Ensure that the material of the IBC is compatible with the chemicals or substances you are transporting. For aggressive chemicals, stainless steel or HDPE containers may be necessary.
- Regulatory Requirements: Certain industries, such as food and pharmaceuticals, have strict regulations regarding packaging. Make sure the IBC you choose meets these standards.
- Cost Efficiency: While rigid IBCs tend to be more expensive initially, their durability and reusability can result in cost savings over time. Flexible IBCs, on the other hand, are typically more cost-effective upfront.
Sustainability & Reconditioning Services
At C.L. Smith, we are committed to promoting sustainability in the packaging industry. Our sister company, Southern Container, a Novvia Group Company, offers IBC reconditioning services that help you meet Environmental Sustainability Reporting (ESR) standards, reduce single-use plastics, and cut costs. With Southern Container, you can enjoy no-cost tote pick-up and storage, eliminating environmental liability while ensuring your IBCs are ready for reuse.

Making the Right Choice for Your Bulk Packaging Needs
Intermediate Bulk Containers (IBCs) are versatile, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly solutions for transporting and storing bulk products. Whether you need rigid or flexible IBCs, the experts at C.L. Smith can help you choose the right solution to fit your specific needs. By considering factors such as material compatibility, product type, and regulatory requirements, you can optimize your supply chain processes and improve efficiency.
If you’re looking for high-quality IBCs for your business or need reconditioning services to reduce costs and environmental impact, contact us today at C.L. Smith. We’re here to help you find the perfect bulk packaging solutions for your products.
Comments are closed